Comprising central Europe, the Czech Republic boasts a rich and extensive history going back to the ninth century. Various emperors and kingdoms have ruled it; it has seen wars and revolutions; at last it acquired its freedom in 1993.
Etymology
The Czech term "Čech," which honors the fable progenitor of the Czech nation, Prince Čech, lends the name "Czech". Once the nation turned into a democratic republic in 1918, the word “Republic" was included in its name.
Early History
Celtic tribes living during the Iron Age were the first known occupants of what is now the Czech Republic. After conquering these areas, the Roman Empire included them in their province of Pannonia in the first century BC. Slavic tribes moved to this area in the sixth century AD and established a number of main kingdoms. Great Moravia was one of these; it developed into a strong state, but there was a mistake in generation. If it keeps on, kindly try once more or get help. In the ninth century, while Prince Rastislav was in charge.
Czechoslovakia
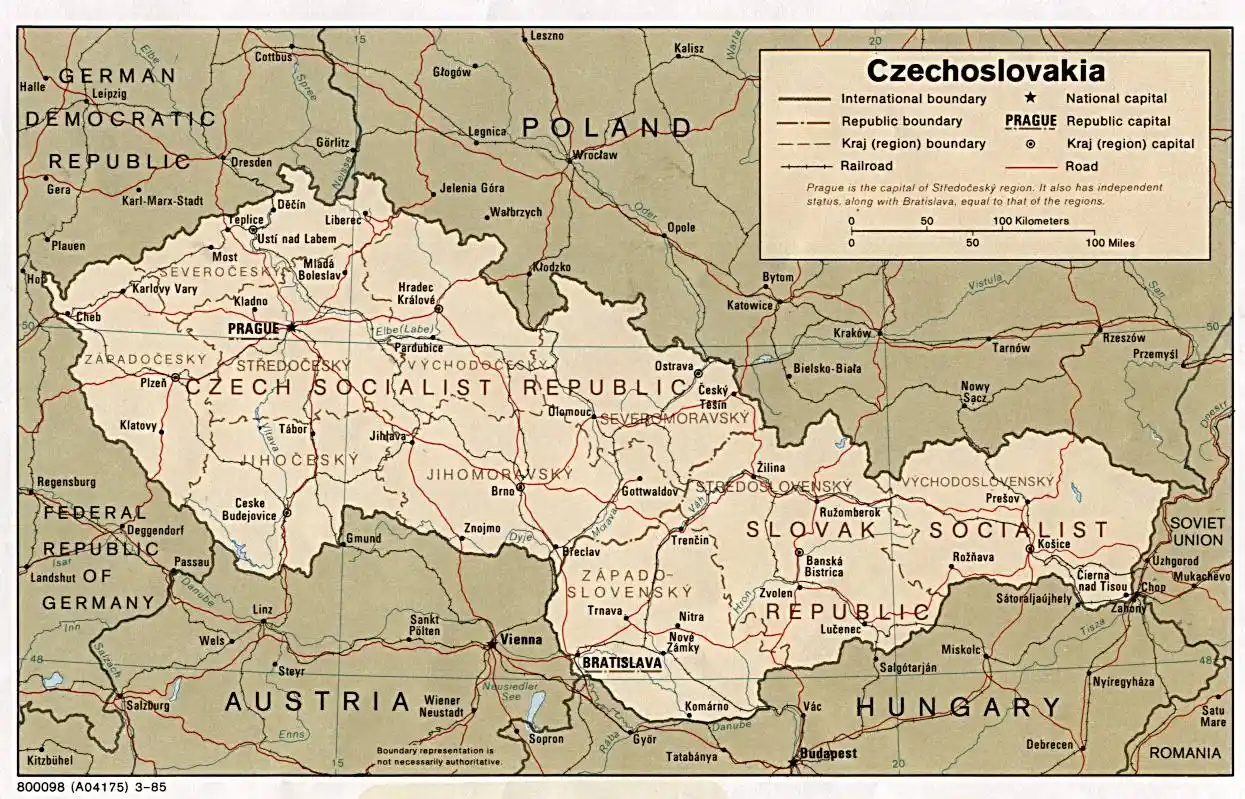
Tenth-century Duke Boleslaus I's rule saw the Czech territories absorbed into the Holy Roman Empire. First Bohemian king, crowned in 1212, King Otakar I Under Charles IV, Bohemia accomplished considerable progress in the fourteenth century. He established Prague as "The Golden City," a cultural and commercial hub. But political unrest and battles after his death degraded the realm. Bohemia came under Habsburg control in 1526 when Ferdinand I was chosen Holy Roman Emperor. Nearly four centuries of Habsburg rule defined the nation.
The Kingdom of Bohemia
Under Duke Boleslaus I, the kingdom of Bohemia first arose in the tenth century. For the Czech lands, this signaled a period of wealth and cultural development. Now, the capital, Prague, has developed into a major trade and educational hub. The kingdom was beset with difficulties, including internal strife among kings and the aristocracy and invasions from surrounding nations. In central Europe, it stayed a potent weapon.
Habsburg Rule
Rising as Bohemian king in 1526, Ferdinand I of Habsburg's family ruled for almost three centuries. German language and culture had a big impact on the Czech land at this period. In the 19th century, movements for emancipation from Habsburg control and nationalism evolved. The Czech people began proudly expressing their own language, culture, and identity.
Czech Republic
Established in 1918 after the Austro-Hungarian Empire fell, Czechoslovakia of Silesia, Moravia, and Bohemia was a democratic First Republic (1918–1939) distinguished by economic growth. Adopted it in 1939, Nazi Germany went on till World War Two. Under the USSR, 1948 saw Czechoslovakia become communist. For its people, this stood for political tyranny and financial pain.
Geography and Culture
A landlocked nation with beautiful scenery, medieval castles, and energetic cities, the Czech Republic is known for its output of beer and wine. German, Slavic, and Jewish customs, among others, have shaped Czech society. Prague, the capital, is a well-known tourism destination for its great architecture and rich past.
Environment
The average temperature in the Czech Republic is low because pleasant summers and cold winters abound. The country features four distinct seasons, which fit outdoor activities rather well.
Biodiversity and Conservation
The Czech Republic boasts a rather wide range of flora and animals. The country features several national parks and nature reserves to help protect its natural wealth.
Government and politics

The head of state is the president of the parliamentary democracy that is the Czech Republic; the head of government is the prime minister. The nation conducts frequent elections and has a multi-party system. Miloš Zeman is its present President. From 2003 to 2013, Petr Pavel presided over the Czech Republic in the first presidency. In steering the nation toward political stability and economic progress, he was rather helpful. In 2001, the Czech Republic government chose its prime minister, whose name was Petr Fiala. Attached to the Civic Democratic Party, he promises to focus on economic recovery and corruption avoidance. Still a democratic country with a robust economy, the Czech Republic keeps shining. Although income disparity and an ageing population present problems, it is working to solve these issues. Celebrating its 28 years of freedom, the Czech Republic remains a proud and energetic nation with a bright future based on history. It is a fascinating place for tourists from all around the world since its people still embrace modernism while also safeguarding their cultural legacy.
Legal system and laws
Based on the Napoleonic Code, the civil law system of the Czech Republic is the nation that boasts a Supreme Court and an autonomous court meant for law interpretation and execution. The Czech Republic's Constitution gives its people basic liberties and rights like those of speech, religion, and assembly, therefore safeguarding their freedom. Different government organizations, including the Office of the Public Defender of Rights, guard human rights.
Foreign relations
Among the several international agencies, the Czech Republic belongs to NATO, the European Union, and the United Nations. Having diplomatic ties with about 190 nations, it maintains amicable relations with its neighbours. The nation also fervently supports democracy, human rights, and global development. It provides foreign aid to poor countries and supports peacekeeping activities.
Military
Mostly focused on defense and international peacekeeping, the professional military force of the Czech Republic comprises the Army, Air Force, and Special Forces. The Czech Republic also supports collective defense projects among other members of NATO.
Human rights
The Czech Republic has notably advanced and protected human rights since gaining its independence. Still, concerns, though, are prejudice against minorities and corruption. The nation has moved recently toward tackling these problems by means of legislative adjustments and anti-corruption initiatives.
Administrative divisions
The Czech Republic boasts thirteen administrative areas, each with a governor and an elected regional parliament. The capital, Prague, is special in that it is a region rather than a part of any other location. Every region is divided into districts; the country boasts 76 districts total. For their citizens, these districts are in charge of offering fundamental services, including public transit, healthcare, and education.
Economy

Strong manufacturing and service emphasis drives the developed and highly industrialized economy of the Czech Republic. It ranks among the most consistent and affluent economies of Central Europe. Electronics, machinery, and automotive production define the key sectors of the country. About 10% of its GDP, tourism also greatly affects its economy.
Industry
Among European producers and exporters of vehicles, the Czech Republic is rather active. Top producers in the nation are Hyundai, Tatra Trucks, and Škoda Auto. Manufacturing, chemicals, and electronics are other vital national sectors.
Transportation
Comprising a large network of airports, trains, and highways, the Czech Republic presents a contemporary transportation infrastructure. Public transport in big cities, including Prague, is rather reasonably priced. The country also features a sizable system of bike routes, which makes local and visitor two-wheel exploration of the country possible.
Communications and IT
With approximately 80% of its people having internet access, the Czech Republic has a high degree of internet penetration. The IT industry of the nation is also fast expanding; big multinational corporations like IBM and Microsoft have their headquarters in Prague. Learning people from all around the world and investors, the country has lately evolved as a magnet for entrepreneurs and digital innovation.
Tourism
Popular for tourism, the Czech Republic features a vibrant culture, outstanding architecture, and rich history. Prague itself draws millions of visitors annually alone. Along with historical landmarks like Cesky Krumlov and resort towns like Karlovy Vary, other well-known locations in the nation include Ecotourism, which has also grown in the nation recently; its stunning national parks and nature reserves draw tourists from all around the world.
Science and Education

Science is a major legacy of the Czech Republic, where many eminent inventions and discoveries have come from its citizens. The nation also has a first-rate education; its universities routinely rank among the best in Europe. All people have free access to primary and secondary education; higher education is more reasonably priced than in other European nations. Furthermore, highly literate in the nation is over 99%.
Culture
Rich in cultural legacy, the Czech Republic not only reflects its own past but also the history of the nations around its current boundaries. The Czech Republic's music, literary, and film sectors also greatly satisfy the Czech people, given that so many artists and works are acknowledged all over the world.
Demographics
With around 10 million residents, the bulk of whom are ethnic Czechs, the Czech Republic has other minorities comprising Vietnamese, Roma, and Slovaks. The low fertility rate and elderly population of the nation raise questions about its future workforce and social security system.
Literature
Packed in the Middle Ages literary tradition, the Czech Republic has two of the most prominent authors, among them are Franz Kafka and Milan Kundera. Prague boasts a rich theater scene thanks in great part to its National Theatre and State Opera.
Religion
Although most of the people of the Czech Republic identify as Roman Catholic, the country has a rich religious past. Other important religious groupings are atheists, Orthodox Christians, and Protestants. Legal protections for religious liberties abound in the nation, yet recently declining religiosity among many people has resulted in many identifying as non-religious or atheists.
Healthcare
Every person living in the Czech Republic has access to reasonably priced healthcare since the country runs a universal healthcare system. Taxes pay for the system, which provides thorough coverage for required medical treatments. Those who can pay for it also have private healthcare alternatives. With a strong focus on preventative treatment and well-being, the nation has a high life expectancy as well.
Cuisine
A big feast of meats, potatoes, and dumplings traditionally forms Czech cuisine. Common dinners ask for knedliky and svickova, cream-sauced beef sirloin. Beer consumption per person in the Czech Republic is the highest among countries. The national beers are Pilsner Urquell and Budweiser.
Sports
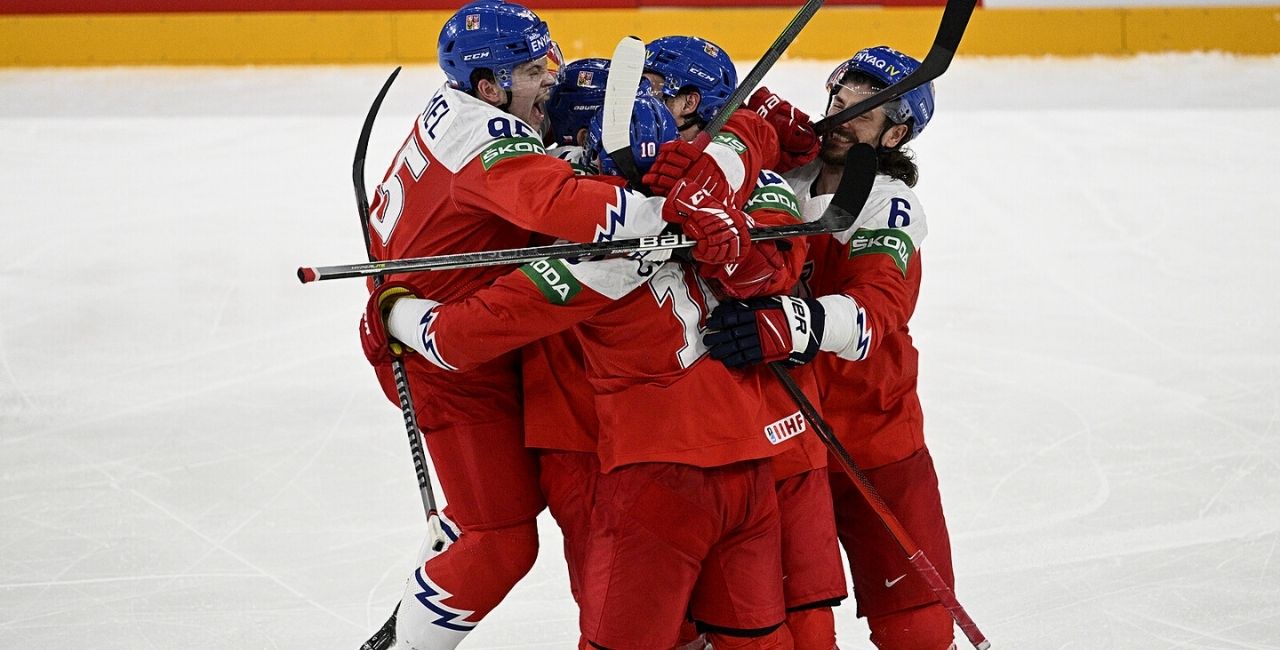

Czech sports are rich; football (soccer) is the most popular among them. Jagr and Kvitova are great non-tennis and ice hockey players. Locals and tourists love hiking, skiing, and cycling.