Small and located in Northern Europe, Denmark. Its rich legacy started in the ninth century with the Vikings' arrival.
Etymology
Danish phrases "Daner" and "Mark" define Denmark's name, therefore referring to "Land of the Danes." Records first mention the phrase about 876 AD.
Viking Age, from 800 to 1050 AD
The Viking Age dominates Denmark's past most of all. Mostly controlling most of modern-day Denmark, Vikings were known for their seafaring expertise and military background. They also raided and colonized England and France, among other areas of Europe. Skilled traders and shipbuilders, the Vikings were able to create rich trading networks and a powerful economy by means of these abilities. Their complicated social system also had chieftains in charge of smaller villages within the bigger Viking culture.
Christianization and Unification (11th century)

Denmark changed radically from paganism to Christianity early in the 11th century. King Harald Bluetooth unified Denmark's several provinces under one authority and brought Christianity to the country. Many magnificent monasteries and cathedrals built in reaction to the introduction of Christianity still rank as major cultural monuments in Denmark today.
Kalmar Union between 1397 and 1523
Politically linked from 1397 until 1523 under the Kalmar Union were Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It centralised the three kingdoms under one ruler and changed Danish politics and culture. Copenhagen started to be the capital of Denmark at this point; its advantageous position on the Baltic Sea allowed trade to bloom.
Reformation (1536)
In 1536, King Christian III made Protestantism Denmark's official religion. Since the crown confiscated church buildings and Catholic monasteries were closed, this marked a dramatic transformation in Danish society. Moreover, the Danish Church was changing significantly during this period.
Absolute Monarchy (1660–1848)
Over the 17th and 18th centuries, Denmark was under definite rulers with complete authority over government and society. Still, Denmark had tremendous cultural and economic growth throughout this time. The monarchy also greatly developed Denmark's foreign holdings, particularly in the Caribbean.
Democracy and Modernity (1848–present)
Denmark adopted a new constitution restricting the king's authority and so granting more liberties to its people in 1849, therefore transforming it into a constitutional monarchy. This readied Denmark for its democratic government, which it currently boasts. Denmark underwent a major social and economic change in the 20th century that modernised the nation and raised the national quality of living. Currently, Denmark is a progressive welfare state with one of the highest levels of life quality worldwide.
Government and politics

Denmark has a multi-party system and a parliamentary democracy, although the head of state is a monarch. Three branches define the government: the legislative, judicial, and executive. Margrethe II, the reigning Queen of Denmark, has been on the throne since 1972 and serves essentially ceremonial functions in the government.
Law and judicial system
Civil law and the ideas of judicial review form the foundation of the Danish legal system. Comprising all subordinate courts, the Supreme Court is the highest court in Denmark.
Danish Realm
Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands taken together form the constitutional monarchy known as the Danish Realm. Although every territory has a parliament and government, they all have a shared monarch and foreign policy.
Administrative divisions
There are five regions in Denmark, each with a regional council in charge of social services, healthcare, and regional development. Further divisions within these areas are 98 municipalities under local administration
Foreign relations
Among other international organisations, Denmark belongs to NATO, the United Nations, and the European Union. Strong diplomatic links with nations all throughout the globe also abound there.
Military
The Army, Navy, and Air Force of Denmark comprise its military. Though it also serves in international peacekeeping operations, it is essentially a defensive force.
Economy and Industry
Denmark has little corruption, a trained workforce, and economic independence, among other things. Among its main sectors are sophisticated manufacturing, medications, and renewable energy. Denmark has also led sustainable development and green technologies since many businesses lower carbon emissions and support environmentally friendly behaviour.
Public policy
The public policy in Denmark is mostly oriented toward social welfare and equality. Among the many perks and services the government offers its people are free healthcare, education, and parental leave. With laws meant to lower carbon emissions and support renewable energy sources, the nation also places great focus on sustainable development.
Labor market
Denmark stresses work-life balance and has a highly competent and efficient workforce. Additionally, among the highest rates in the world for union membership in the nation, it helps defend workers' rights and negotiate reasonable salaries.
Business

Denmark's business environment is welcoming; low corporate taxes and simplified bureaucracy help to explain this. Among its main businesses are advanced manufacturing, drugs, and renewable energy. Furthermore, the nation is well-known for its entrepreneurial energy and powerful startup scene.
Science and technology
Denmark's research and development are much appreciated; funding science and technology advances the nation.
Energy
By 2030, Denmark wants all of its electricity to come from renewable sources. Apart from boosting wind energy, the country is also looking at solar and biogas.
Transport
Denmark features a contemporary and effective transport infrastructure with airports, trains, and a vast road network. The country is particularly well-known for its environmental travel rules; several cities support cycling as the major form of mobility.
Geography and Culture
For all its modest stature, Denmark boasts beautiful beaches, flat fields, and softly rising hills. Viking, Christian, and modern European inspirations characterise its eclectic culture. Design brands The LEGO Company and Bang & Olufsen, as well as warmth and traditional cuisine like smørrebrød, are passions of Danes.
Climate
Denmark boasts nice summers and cold winters. The Baltic and North Sea location of rain and wind guarantees their persistent nature.
Ecology
The environmental sustainability of Denmark is well-known even on a small scale. It has pushed ecologically friendly projects and the growth of renewable energy sources.
Environment

Denmark also provides amazing natural settings with perfect beaches, beautiful woods, and gorgeous islands. Numerous national parks and wildlife reserves feature a range of plants and animals.
Demographics
With more than 5.8 million inhabitants, most of whom reside in cities, Denmark has a decent quality of living and is well-known for its robust social assistance program, therefore giving fair opportunities for all people. Though English is spoken and understood somewhat generally throughout Denmark, Danish is the official language. The country also boasts a mixed population with notable immigration groups from all throughout the world.
Languages
Other languages spoken in Denmark apart from Danish, German, Faroese, and Greenlandic are many. Many Danes also speak English relatively fluently, which promotes national trade and interaction abroad.
Religion
Denmark is mostly Christian, as so many Danes claim membership in the Lutheran Church of Denmark. Still, the country has a religious diversity with substantial percentages of Muslims, Jews, and Buddhists.
Education
Denmark offers a very sophisticated educational system whereby every citizen can access free education. While primary and secondary education are mandatory, higher education choices include vocational colleges and universities. The nation has a high literacy rate as well, since almost all of its citizens can read and write.
Culture
Denmark has a rich cultural past blending aspects of German and English civilisations with Scandinavian roots. Apart from its literary, musical, and film sectors, the nation is well-known for its architecture and design.
Tourism
Denmark's stunning cities, great landscape, and rich cultural past bring millions of visitors every year. Between them are Aarhus, Copenhagen, and LEGOLAND Theme Park. Among the outdoor pursuits the nation provides are hiking, bicycling, and sailing.
Cuisine
Particularly salmon and herring, stent flask—fried pig belly—frikadeller, which are meatballs, and smørrebrød, which are open-faced sandwiches, are all foods thought to be classic Danish fare. The country is also somewhat well-known for the quality of its seafood.
Human rights
Denmark shows a great will to protect and forward the liberties and rights of its people since it has policies in place to do so. Progressive points of view define the country on issues such as gender equality, LGBTQ+ rights, and freedom of speech.
Sports
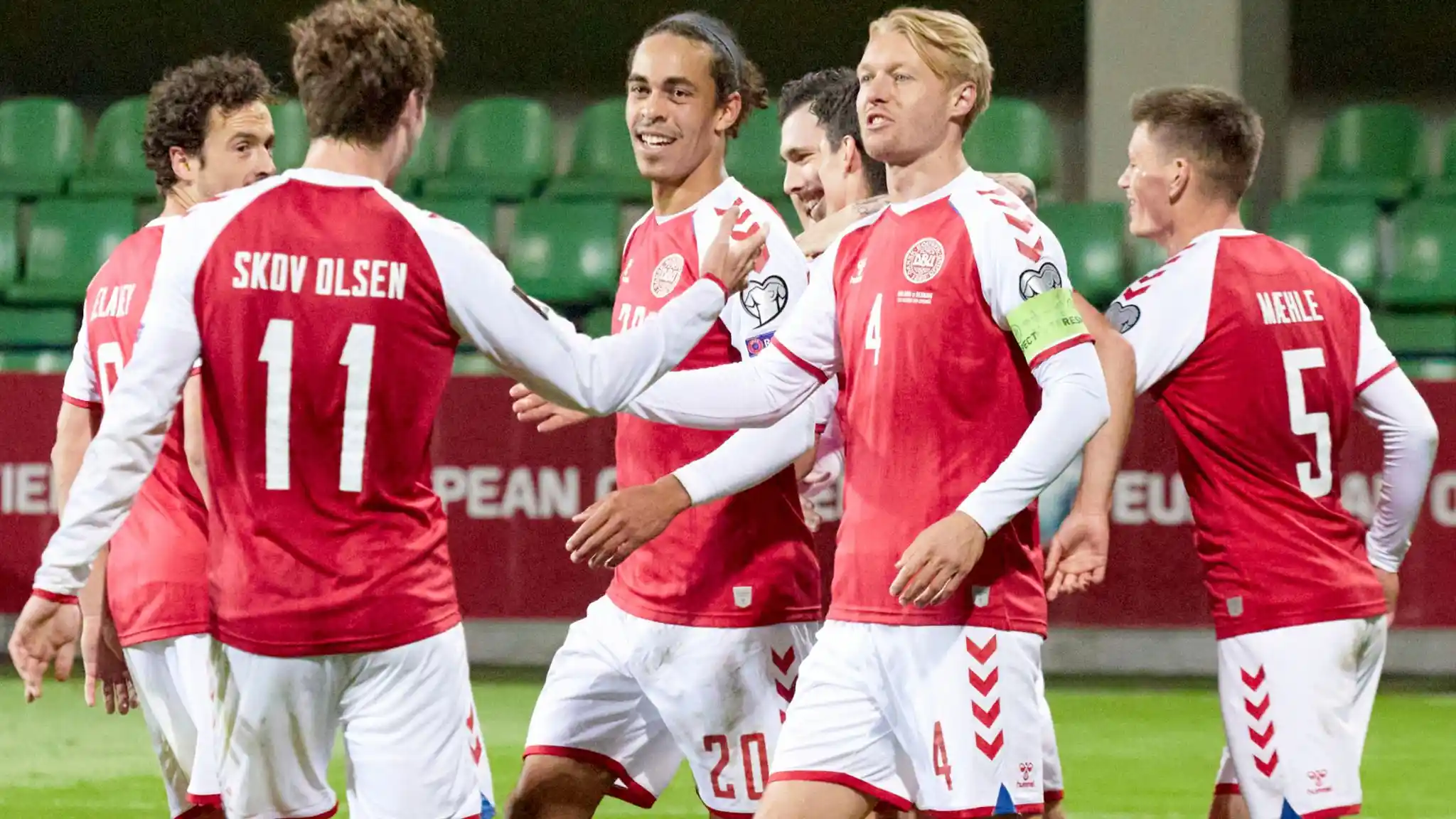

Sports define Danish society largely; the most typically utilised are cycling, handball, and football (soccer). Among the numerous outstanding sportsmen and teams the nation has developed are the national handball team and football player Christian Eriksen.